An early diagnosis means early treatment and a better chance of a positive result.
Patient end results are often better when a disease is diagnosed and also cured early; however, some diseases do not trigger symptons until a patient is already sick– ovarian cancer, for instance, can go undiscovered for ten years or more, providing it time to infect other organs.
By screening healthful patients for these sneaky illnesses, doctors can discover them earlier– and recent artificial intelligence (AI) instruments guarantee to aid in the hunt.
Cardiovascular diseases
The difficulty: Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) exterminates nearly 18 million individuals annually, making them the leading cause of death globally.
If a doctor knows their patient is at high risk of developing or passing away from a CVD, they can suggest medications or lifestyle changes to lower the danger, but individuals with these illnesses always feel fine– until they have a cardiovascular disease or stroke.
The status quo: Medical professionals could forecast CVD danger making use of devices such as the Framingham Risk Scores structure, yet one of the inputs needed is cholesterol level. That means patients have to go to a clinic to have blood drawn– nobody enjoys that, and also, around a quarter of adults accept they’re afraid of needles.
Previous research study recommends that the width of the blood vessels and also arteries in the retina at the back of the eye can serve as an early indicator of CVD. Yet, professionals must analyze the pictures, indicating there isn’t a basic means to utilize the info to assist a lot of patients.
Cardiovascular diseases are the leading cause of death globally
The AI: For a freshly released research study, UK researchers trained an AI to forecast a patient’s danger of developing CVD based on retinal pictures and danger factors such as age, cigarette use, and medical history– no new blood work required.
To confirm their AI-based model– QUARTZ, or “Quantitative Analysis of Retinal vessels Topology as well as size”— they predicted the CVD threat of nearly 6,000 individuals (average age 67) included in a UK research study trackling long-term health.
The scientists followed to the participants for an average of 9.1 years and discovered that their AI had the ability to predict CVD danger about as accurately as the commonly used Framingham structure.
Looking ahead: The participants in the UK were predominantly white and with a way of livings healthier than typical for their location and age, so the AI still requires to be confirmed on a broader populace.
And also, while retinal imaging is common as well as inexpensive, it does require specialized tools, commonly operated by an ophthalmologist. Cardiologists and General practitioners will require to figure out the best way to bring this sort of imaging into their workflows.
Nonetheless, research study into making use of smartphone cameras for retinal imaging could streamline the process– this current AI might one day be included into an app that allows people to examine their CVD threat without going through any kind of invasive testing or even leaving their houses.
Breast cancer
The obstacle: Breast cancer is one of the most common cancer worldwide, but thanks to effective therapies, it’s not one of the most deadly– while survival rates vary by place, 90% of patients in high-income countries survive 5 or even more years after diagnosis.
Early discovery is vital to those favorable results. If the cancer is discovered while still localized to the breast, the 5-year survival rate in the United States is 99%; however, if it has already spread distant parts of the body, such as the lungs or liver, the rate drops to just 29%.
The status quo: If an individual goes to above-average threat of creating breast cancer, their doctor may suggest that they obtain a breast MRI, in addition to routine mammograms (the criterion screening tool for breast cancer).
Since MRIs are a lot more delicate, they can pick up suspicious lesions that a mammogram may miss. This sensitivity likewise leads to a lot of false positives, which are typically just recognized after the patient undergoes an intrusive tissue biopsy.
The AI could have minimized unnecessary biopsies for as much as 20% of individuals
The AI: Researchers at NYU and Jagiellonian College in Poland used 20,000 breast MRI scans to train an AI to anticipate a patient’s possibility of having breast cancer based on the photos.
Once it was trained, the AI had the ability to anticipate cancer from MRI checks with about the same precision as a panel of five human radiologists.
When the scientists tasked the AI with analyzing scans of BI-RADS category 4 lesions– ones deemed suspious enough that biopsies must be taken into consideration– they discovered that its suggestions would have decreased unnecessary biopsies for up to 20% of pations.
Looking ahead: White individuals accounted for almost 70% of the MRI scans used to train the AI and also for most of those used to evaluate it, so more research study is needed to ensure it’s as accurate at anticipating brast cancer possibility in scans from non-white patients.
If those research studies discover the AI is affective across the populace, it has the potential not just to decrease unnecessary biopsies but likewise assist more breast cancer patients obtain diagnosed.
That’s because the high rate of false positives is a major reason MRI scans aren’t advised for the general population. If an AI can reduce that rate, the scans might come to be a common typical screening tool, assisting more patients achieve earlier diagnoses.
Colorectal cancer
The challenge: Colorectal cancer is the third most typical cancer globally and the 2nd most deadly– just lung cancer kills more individuals.
It starts with the formation of tiny growths, called polyps, on the internal lining of the colon or rectum. Polyps that can come to be cancerous with time are called adenomas, as well as if they aren’t eliminated, the cancer cells can spread beyond the bowel.
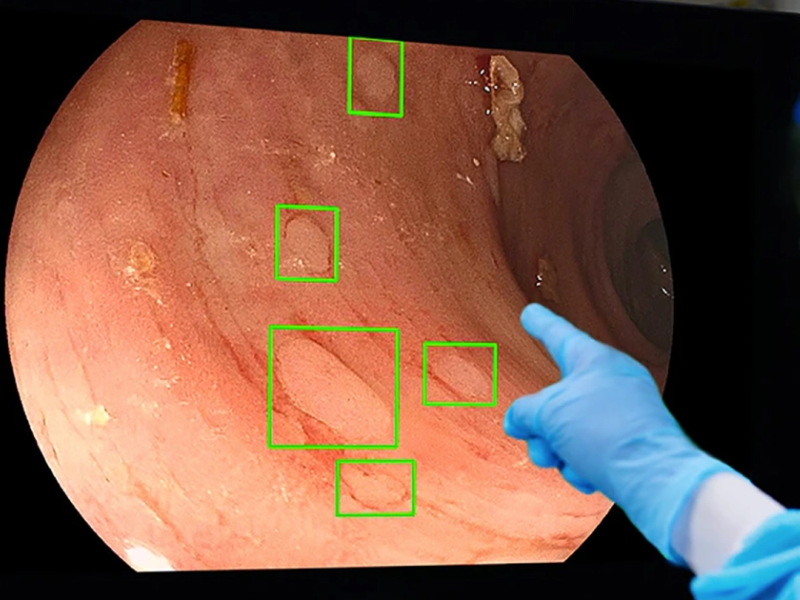
The status quo: One of the most sensitive screening examinations for colorectal cancer is a colonoscopy, a procedure in which a doctor inserts a video camera on a thin, flexible tube into the bowel so that they can scan it for polyps.
Docctors can usually eliminate any polyps they detect during the colonoscopy; however, an approximated 25% of the growths are missed on during the treatment– as well as a small missed polyp can develop into a large problem by the time a person undergoes another screening.
Polyps were missed in half as several patients when the AI was utilized during the initial colonoscopy
The AI: Health tech company Medtronic used pictures of 13 million polyps to train an AI called GI Genius to find them in a colonoscopy camera’s feed– in real-time.
They tested the AI by having 230 people in the United States, UK, and Italy go through two colonoscopies in a single day: in one colonoscopy, the doctor worked alone, and during the other, the AI helped them spot polyps.
When the AI-assisted colonoscopy was first, the physician working alone spotted missed polyps in only 15.5% of patients during the second colonoscopy. When the unassisted doctor went first, however, polyps were located in 32.4% of patients during the AI-assisted treatment.
Looking ahead
Unlike the formerly mentioned AIs, GI Genius isn’t going to save anyone from undergoing an invasive treatment– colonoscopies just are our ideal line of defense against colorectal cancer– but it could, at least help ensure those procedures are less most likely to miss crucial indications of cancer.
GI Genius likewise differs in that it’s already being utilized to help patients, outside of trials– the FDA gave Medtronic authorization to begin marketing the AI as a way to aid spot colorectal cancer in April 2021, as well as it can currently be found at many clinics throughout the US.
Medtronic has additionally teamed with the American Sociaty for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy as well as Amazon Web Services (AWS) to distribute 50 GI Genius systems to healthcare centers in low-income and underserved areas, assisting guarantee more fair access to the potentially life-saving AI.
Read The Original Article On FREETHINK.
Read More: Hubble Space Telescope Reveals Webb A Thing Or Two With Magnificent Recent Image