Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers have developed a compact multi-petawatt laser that uses plasma transmission gratings to overcome the power restrictions of traditional solid-state optical gratings. The design might allow the construction of an ultrafast laser up to 1,000 times more potent than existing lasers of the same dimension.
Petawatt (quadrillion-watt) lasers rely on diffraction gratings for chirped-pulse amplification (CERTIFIED PUBLIC ACCOUNTANT), a strategy for extending, amplifying, and then pressing a high-energy laser pulse to prevent damaging optical parts. CPA, that won a Nobel Prize in physics in 2018, is at the heart of the National Ignition Center’s Advanced Radiographic Capability and NIF’s precursor, the Nova Laser, the world’s first petawatt laser.

The chirped-pulse amplification technique makes it possible for a petawatt laser’s high-power pulses to pass through laser optics without damaging them. Before amplification, low-energy laser pulses are passed through diffraction gratings to stretch their duration by as much as 25,000 times. Thus their peak power is reduced and optics that the pulses pass through remain intact. After amplification, the pulses are recompressed back to near their original duration. Credit: The Nobel Committee for Physics
With a damage limit several orders of size larger than conventional reflection gratings, plasma gratings “enable us to deliver a lot more energy for the same size grating,” stated former LLNL postdoc Matthew Edwards, co-author of a Physical Review Applied paper describing the new style released online on August. 9. Edwards was joined on the paper by Laser-Plasma Interactions Team Leader Pierre Michel.
“Glass focusing optics for powerful lasers must be huge to prevent damage,” Edwards said. “The laser power is spread out to keep local intensity low. Because the plasma resists optical damage better than one piece of glass, for instance, we can imagine developing a laser that produces hundreds or thousands of times as much power as a current system without making that system bigger.”
LLNL, with 50 years of experience developing high-energy laser systems, has also been a longtime leader in the design and fabrication of the globe’s largest diffraction gratings, like the gold gratings used to generate 500-joule petawatt pulses on the Nova laser in the 1990s. Still bigger gratings, nonetheless, would be required for next-generation multi-petawatt and exawatt (1,000-petawatt) lasers to overcome the limits on optimum fluence (energy density) imposed by conventional strong optics (see “Holographic Plasma Lenses for Ultra-High-Power Lasers”).
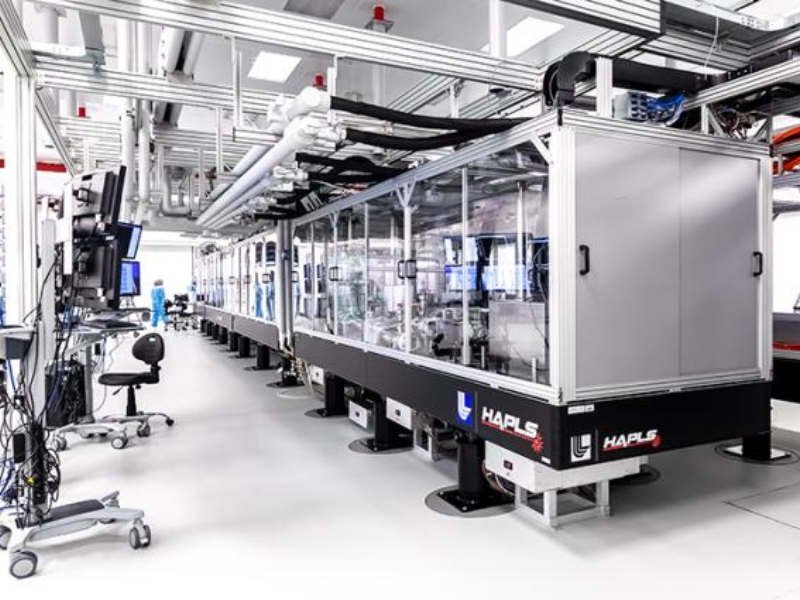
Edwards noticed that optics made of plasma, a mix of ions and free electrons, are “well suited to a relatively high-repetition-rate, high-average-energy laser.” The new design could, for instance, make it possible to field a laser system similar in dimension to the L3 HAPLS (High-Repetition-Rate Advanced Petawatt Laser System) at ELI Beamlines in the Czech Republic but with 100 times the peak energy.
Designed and created by LLNL and delivered to ELI Beamlines in 2017, HAPLS was designed to produce 30 joules of power in a 30-femtosecond (quadrillionth of one second) pulse duration, that is equal to one petawatt and do so at ten Hertz (10 pulses per second).
“If you imagine trying to construct HAPLS with 100 times the peak energy at the same repetition rate, that is the kind of system where this would be most suitable,” stated Edwards, presently an assistant Professor of mechanical engineering at Stanford College.
“The grating can be reprised at a very huge repetition rate, so we think that ten Hertz operation is possible with this kind of design. Nevertheless, it would not be suitable for a high-average-energy continuous-wave laser.”

While plasma optics have been utilized successfully in plasma mirrors, the scientists said their utilization for pulse compression at high energy has been limited by the difficulty of creating a sufficiently consistent large plasma and also the complexity of nonlinear plasma wave dynamics.
“It has proven hard to obtain plasmas to do what you desire them to do,” Edwards said. “It is difficult to make them sufficiently homogenous, to get the temperature and density variations to be small enough, and so on.”
“We are aiming for a design where that kind of inhomogeneity is as small a problem as possible for the total system– the design should be very tolerant to imperfections in the plasma that you use.”
Based on simulations using the particle-in-cell (PICTURE) code EPOCH, the researchers stated, “we expect that this approach is capable of offering a degree of security not available with other plasma-based compression mechanisms and may prove more feasible; to construct in practice.” The new design “requires only gas as the initial tool, is durable to variations in plasma conditions, and minimizes the plasma quantity to make sufficient uniformity practical.”
“By utilizing achievable plasma parameters and avoiding solid-density plasma and solid-state optics, this approach provides a feasible path toward the next generation of high-energy laser.”
Read the original article on lasers LLNL.